5 minutes
WannaCry - Analyzing Initial Stage
Preface
In the early summer of 2017, WannaCry was unleashed on the world. Widely considered to be one of the most devastating malware infections to date, WannaCry left a trail of destruction in its wake. WannaCry is a classic ransomware sample; more specifically, it is a ransomware crypto worm, which means that it can encrypt individual hosts and had the capability to propagate through a network on its own. Here’s my own analysis of this particular specimen.
In this blog post, I will analyze the initial stage of WannaCry ransomware sample. Please note that I’m new at this and I will try to provide a detail technical analysis of the initial stage to the best of my abilities. Hope you will enjoy this!!
Basic Static Analysis

ℹ️ | For this part I used a command line tool named floss to get the strings from the ransomware executable.
By looking as some of the strings, we can see some interesting library related to encryptions such as:
CryptAcquireContextACryptGenRandomCryptServiceACryptReleaseContextCryptGenKeyCryptDecryptCryptEncryptCryptDestroyKeyCryptImportKey
We can also see that the malware will probably modify or add some registry based on the library imported
In the strings, we can also find words such as :
mssecsvc.exe(already flagged for been used for ransomware infection)tasksche.exe
We also see alot of base64 encoded strings
We can see some randomly named folder that will dynamically named on runtime
C:\%s\%sC:\%s\qeriuwjhrf
We can also some interesting urls, such as :
http://www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com
An interesting string that let’s us know for sure that we’re dealing with the WannaCry malware :
c.wnryt.wnrymsg/m_croatian.wnrymsg/m_dutch.wnry9msg/m_english.wnryFmsg/m_korean.wnrymsg/m_latvian.wnry
Interesting strings:
115p7UMMngoj1pMvkpHijcRdfJNXj6LrLn12t9YDPgwueZ9NyMgw519p7AA8isjr6SMw13AM4VW2dhxYgXeQepoHkHSQuy6NgaEb94
Suspicious commands:
icacls . /grant Everyone:F /T /C /Q(Granting everyon acces to ACL)
Basic Dynamic Analysis
- When triggering the malware with internet nothing happens, as far as encrypting my files, but I see that some calls are made to a malicious url, probably to drop something else on my file system
- When triggering the malware without internet connection, i can see that my file system get automatically encrypted
- There’s seems to be a lot of call to different DNS
Triggering the malware with fake internet simulation
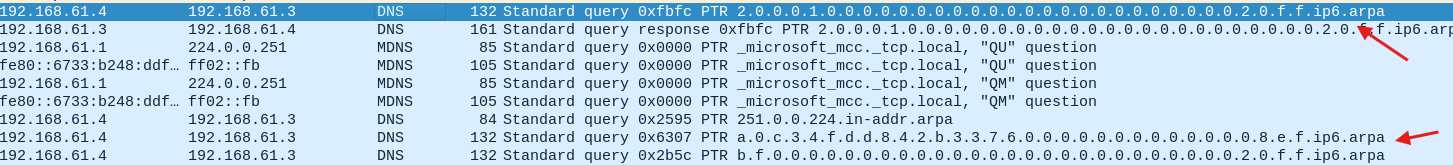

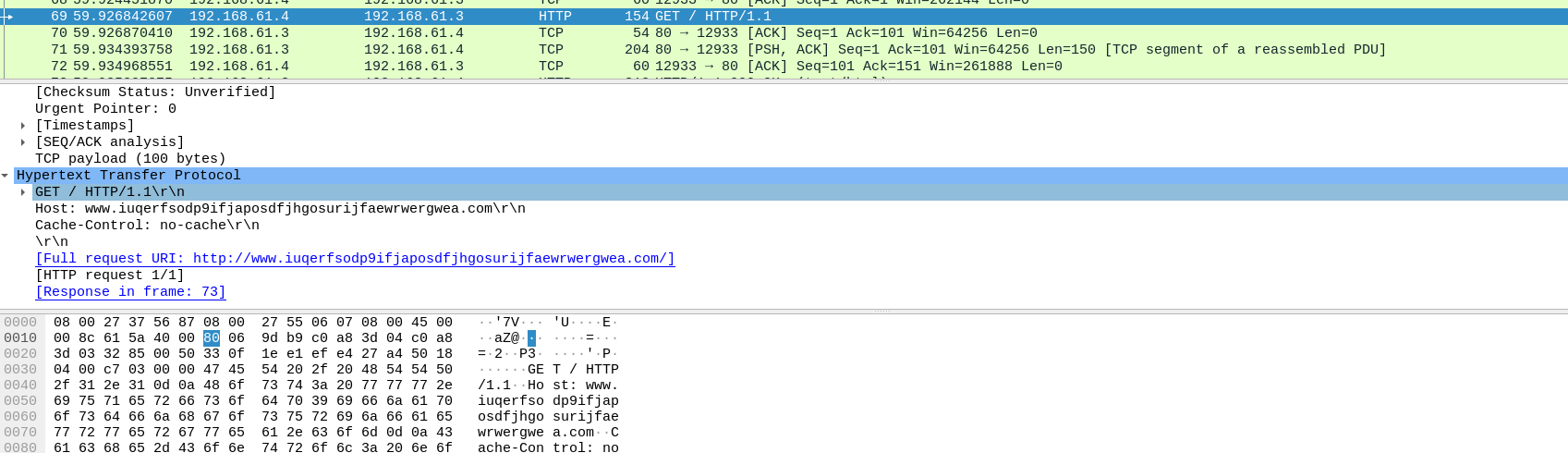
- It seems that the malware is making an http request to a malicious url
Triggering the malware without internet simulation
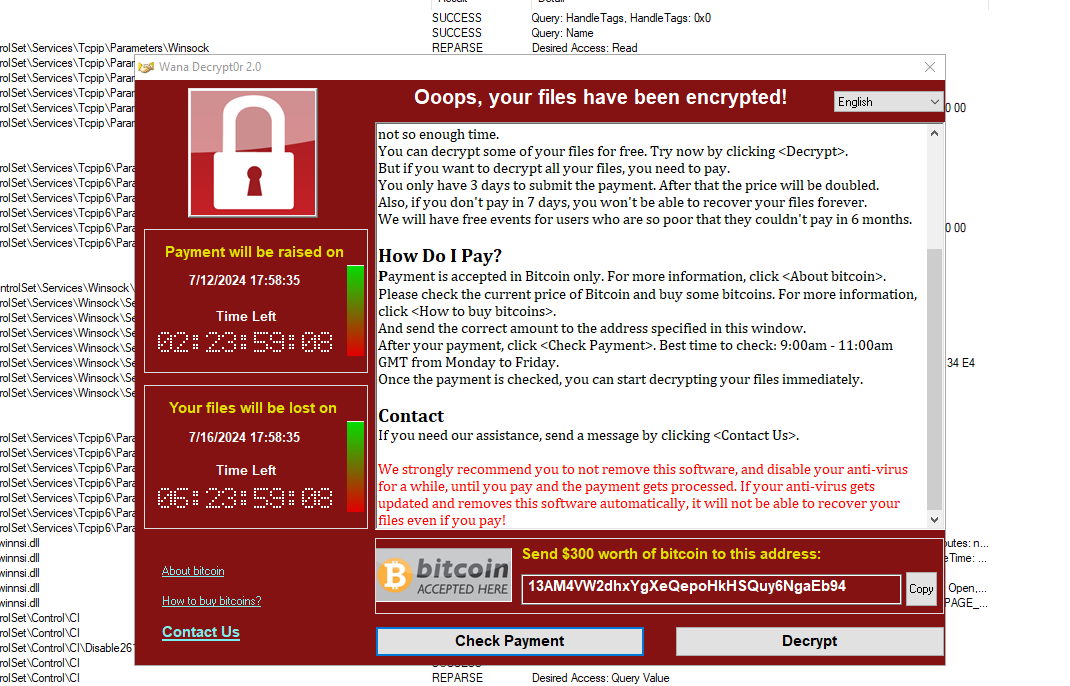
- A window pops up, that asks for payment and all my files are now encrypted
- There’s new executable for decryption being created on my desktop
@WanaDecryptor@.exe
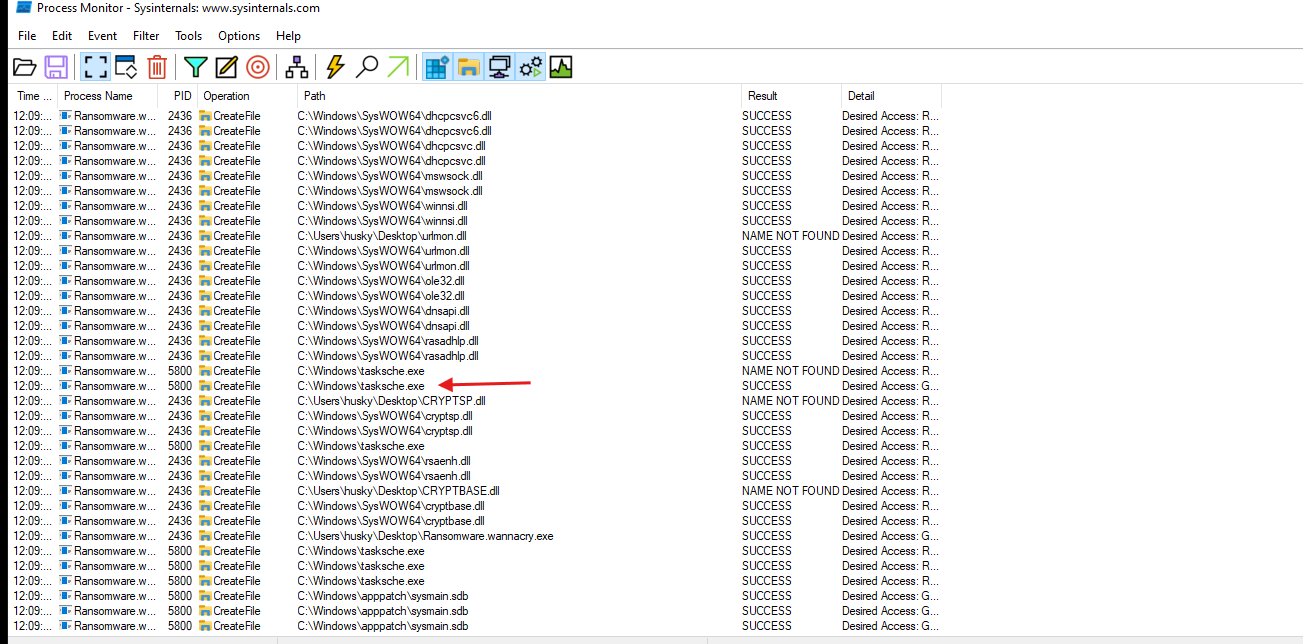
- a new executable is created named :
tasksche.exe
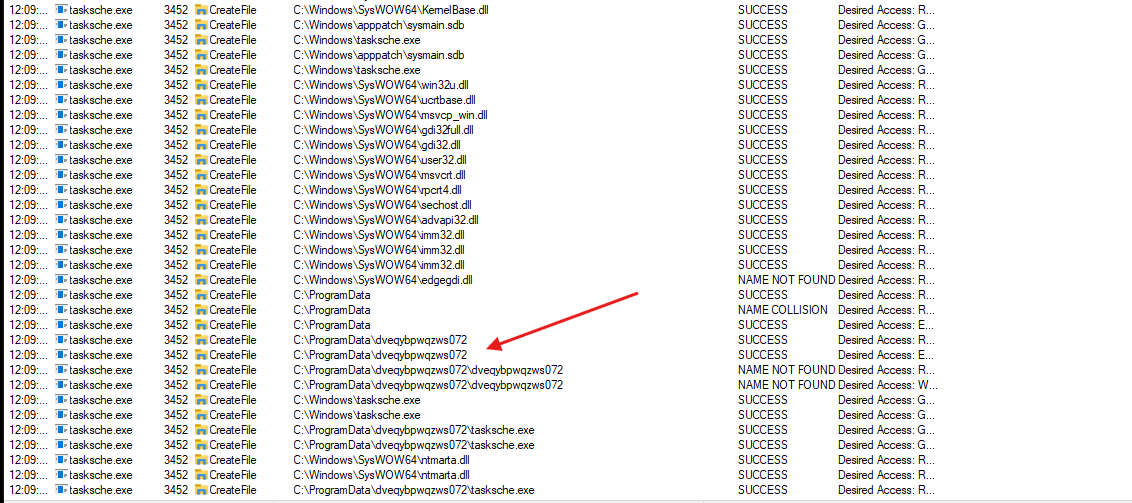
- we can also see that a folder is created by this newly executed process
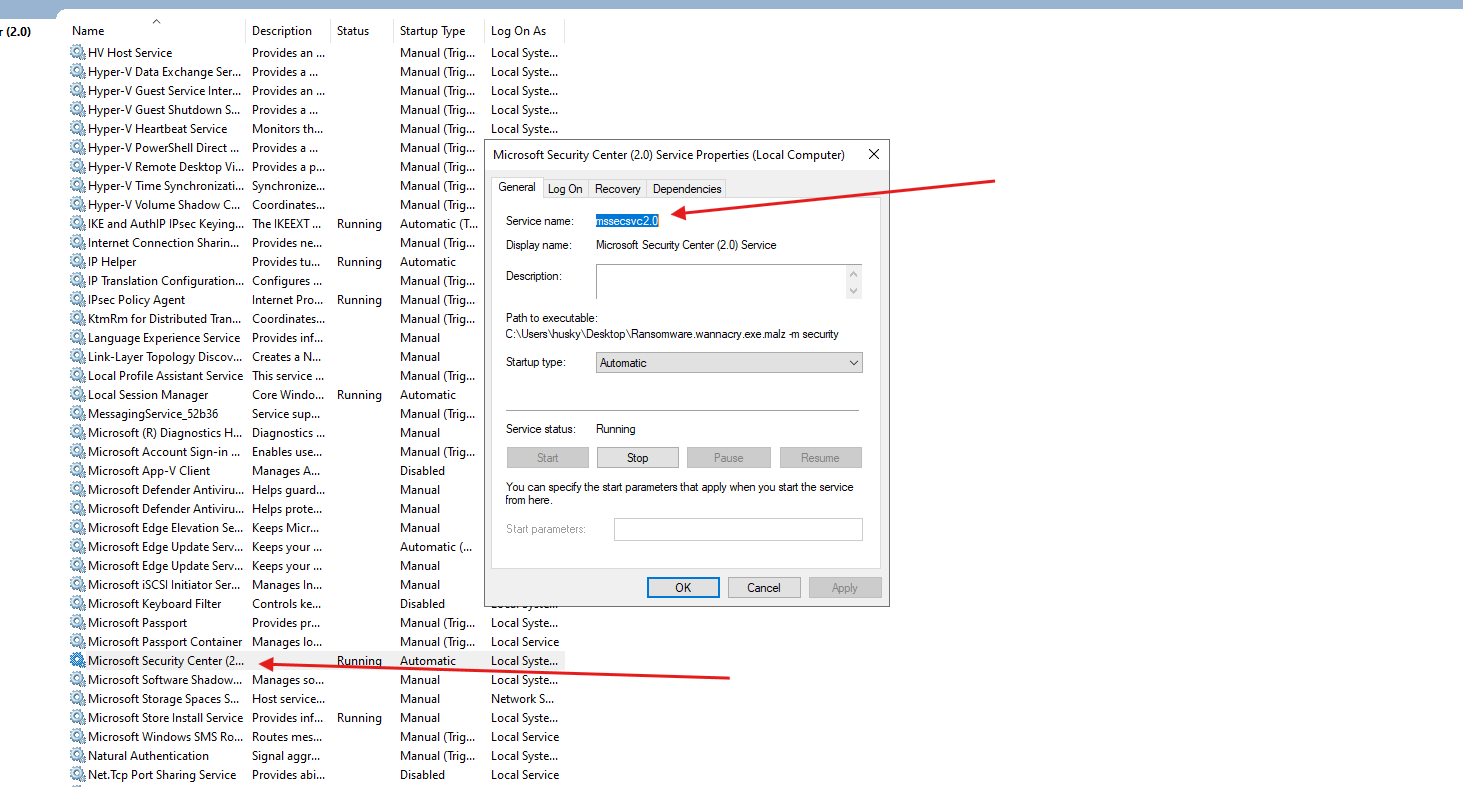
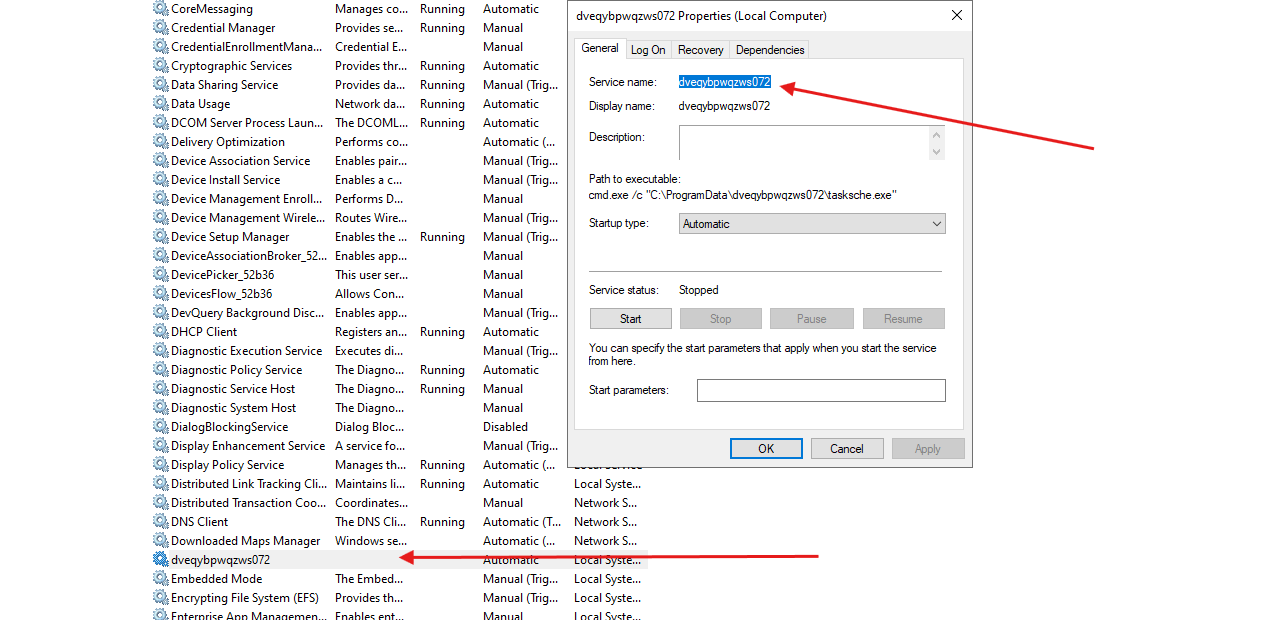
- We also see that 2 new services have been created
mssecsvc2.0dveqybpwqzws072
Advanced Static Analysis
ℹ️ | In this section, I will be using cutter and ghidra for the advanced static analysis
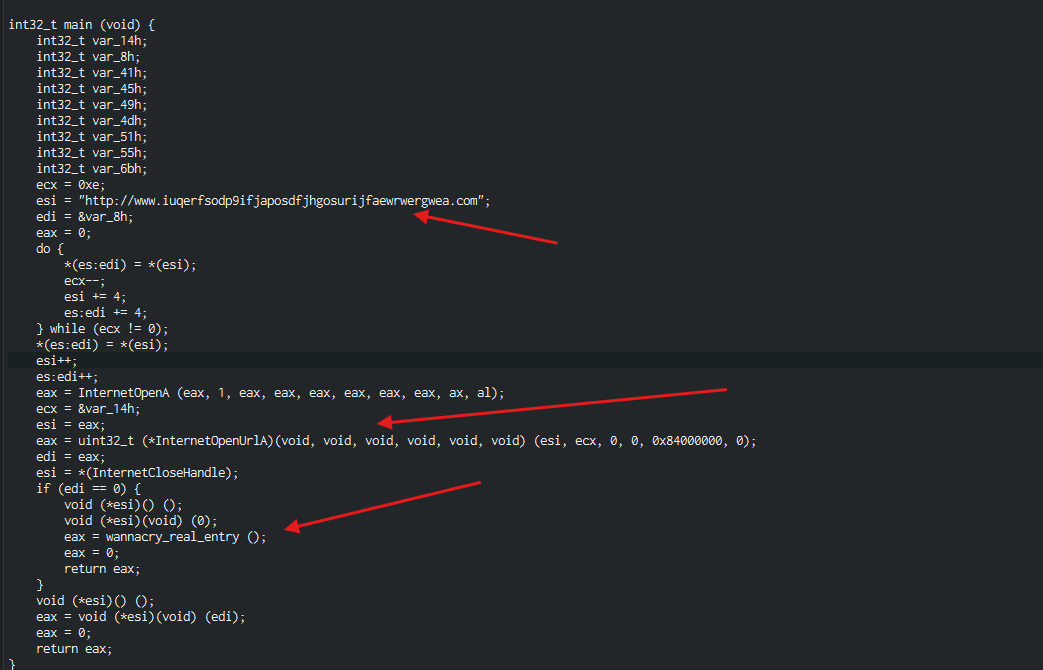
- Here we can see that based on the response from the malicious domain, we will enter the real program
- Option 1 : We received a response from the domain and the program execute normally
- Option 2: We receive no response and the WannaCry program gets executed
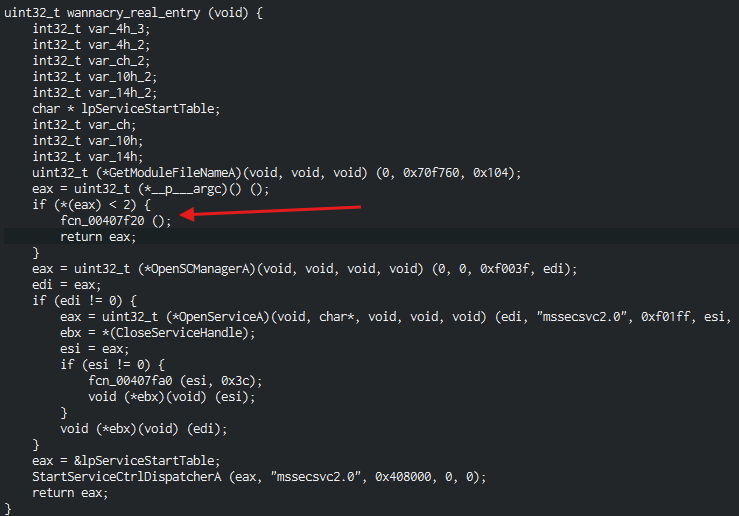
- based on the numbers arguments received we will enter in this function
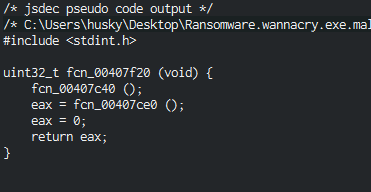
- Here there’s two function available, we will enter in the first one
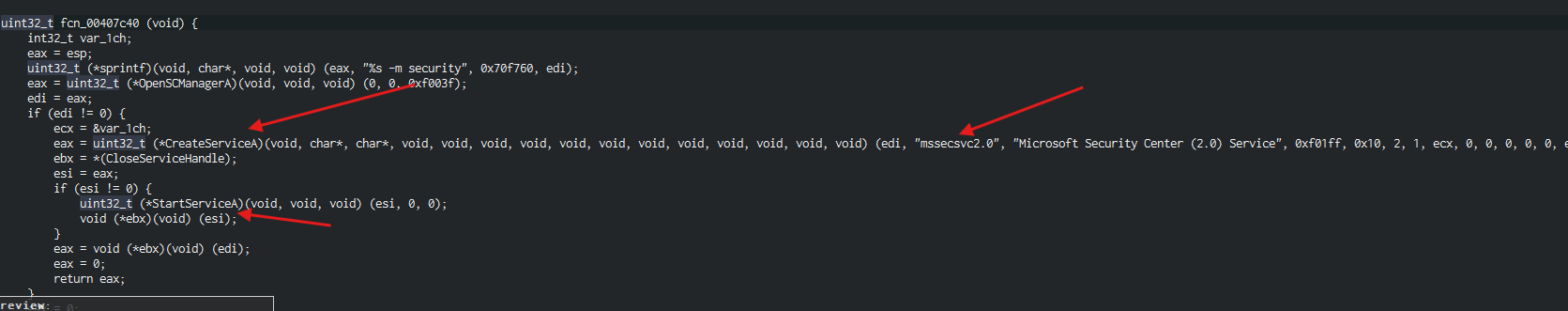
- Here we can see that the malware is creating and starting a new service called :
mssecsvc2.0
⚠️ | The second function will be analyzed via ghidra, since it was difficult to debug it in cutter
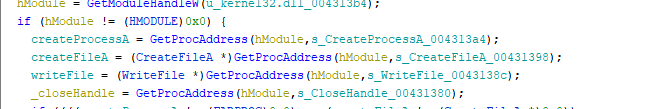
- Here we can see that 4 function are loaded from
kernek32.dll, will probably be used to create a malicious process that will run on the host machine
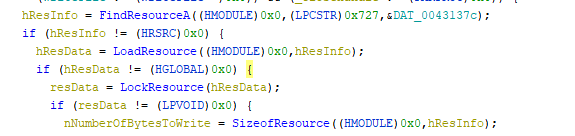
- Here we can see that a resource is loaded, let’s wait and see what it will be used for
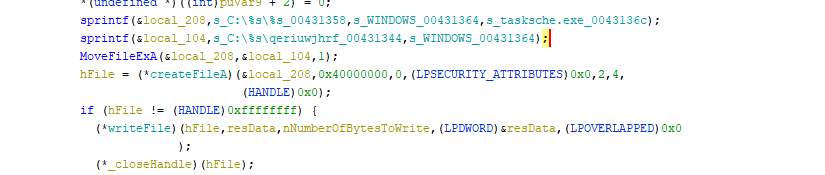
- In the first 2 lines containing the
sprintfstatement we’re formatting some strings - The line containing the
MoveFileExA, to rename a file
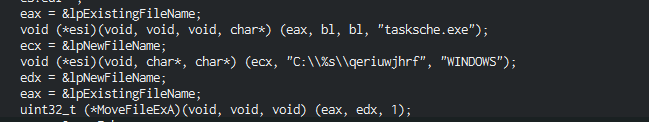
- By comparing the same lines in cutter, we can clearly see that the malware is renaming the temporary file
qeriuwjhrftotasksche.exe - Then we’re creating the file named
tasksche.exe - Finally we can see that the program is writing the resource that was loaded earlier in the newly create file named
tasksche.exe
Advanced Dynamic Analysis
ℹ️ | Since I covered most of the initial program of the WannaCry program, in this section I just wanted to see how the newly created executable would be run. I used the famous debugger x32dbg
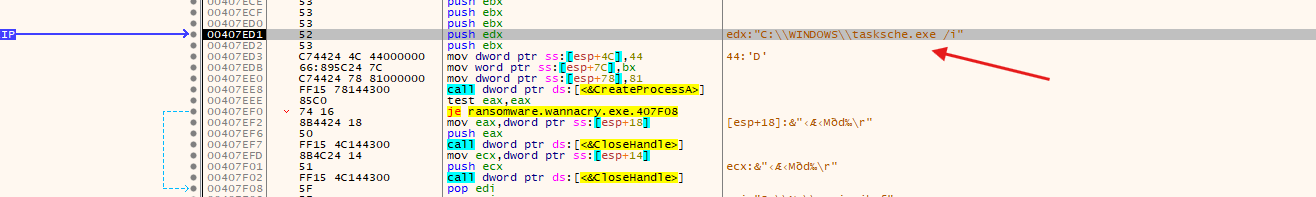
- Here we can see that the file
tasksche.exewill be executed with the/i. This is the program that starts the encryption process.
Rules & Signatures
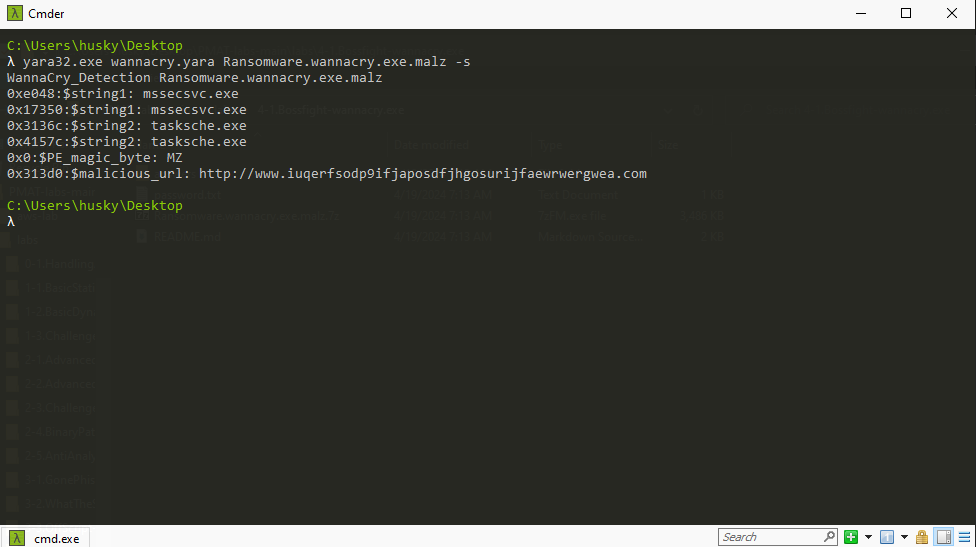
rule WannaCry_Detection {
meta:
last_updated = "2024-07-16"
author = "8erg"
description = "Yare detection rule for WannaCry Ransom"
strings:
$string1 = "mssecsvc.exe"
$string2 = "tasksche.exe"
$PE_magic_byte = "MZ"
$malicious_url = "http://www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com"
condition:
$PE_magic_byte at 0 and
($string1 and $string2) or
$malicious_url
}
Conclusion
To conclude, this analysis was done following a certification that i went through recently and it is called Practical Malware Analysis & Triage. Even though, this is an old ransomware and many research has been peroformed onit. I still think that it was a great learning curve for me and I really enjoyed walking through the steps of the malware author and seeing how this ransomware worked.
863 Words
2024-07-15 17:00